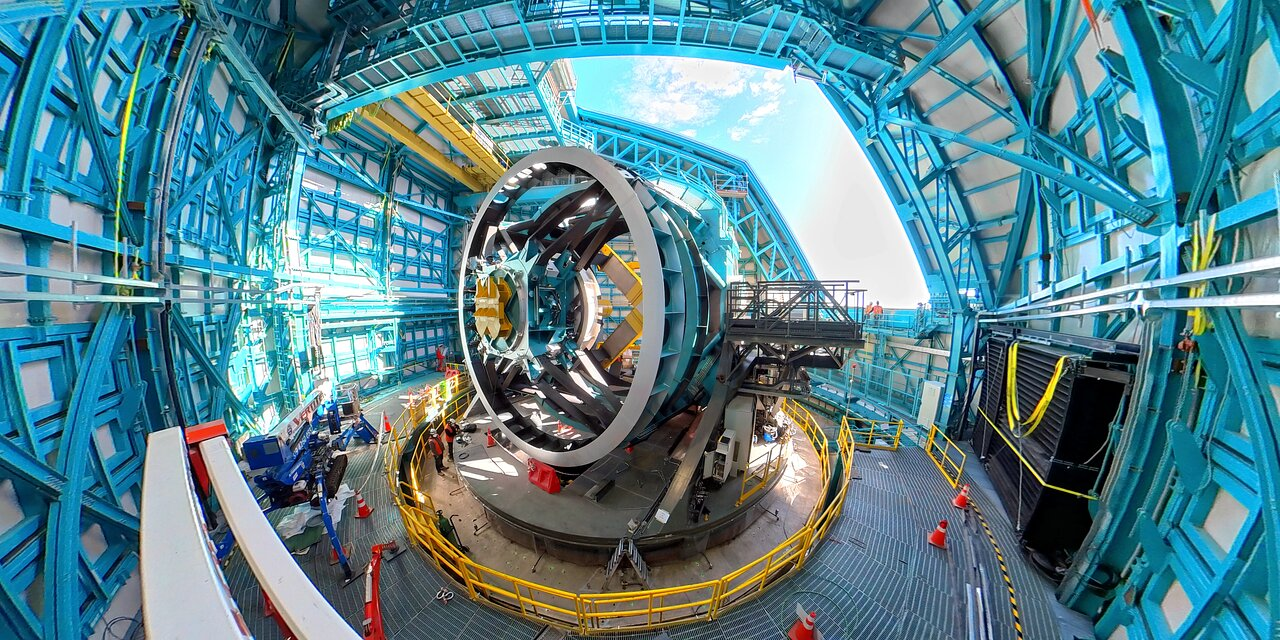
Rubin Observatory is at the forefront of modern astronomy, aiming to unveil the mysteries of the universe through its groundbreaking Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) project. This ambitious initiative is set to revolutionize astronomical imaging, utilizing the powerful LSST Camera to capture stunningly detailed images of the night sky. By systematically mapping the Milky Way and probing the elusive nature of dark matter, Rubin Observatory will provide invaluable insights into cosmic phenomena. The observatory’s innovative approach combines advanced imaging technology with a comprehensive data-sharing strategy, ensuring that the scientific community can explore celestial mechanics like never before. As we embark on this exhilarating journey of cosmic cinematography, the Rubin Observatory promises to illuminate the grandeur of space, one astronomical image at a time.
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory represents a significant leap forward in our quest to better understand the cosmos. With its cutting-edge Legacy Survey of Space and Time, this facility aims to capture extensive and detailed views of the skies, leveraging the capabilities of its advanced imaging device known as the LSST Camera. Through continuous monitoring of celestial dynamics and mapping of our galactic home, scientists hope to unlock new knowledge about dark matter and other intricate cosmic puzzles. The project encourages broad collaboration across the scientific community, facilitating access to a wealth of astronomical data. This innovative strategy not only focuses on exploring astronomical phenomena but also emphasizes public education and outreach, making the wonders of the universe accessible to millions.
Introduction to the Rubin Observatory and its Mission
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, situated in Chile, is spearheading a groundbreaking initiative known as the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). This ambitious ten-year project aims to create a comprehensive map of the universe, showcasing a plethora of astronomical phenomena, including the elusive dark matter that plays a crucial role in cosmic structure. With its unparalleled 144-megapixel test camera, the observatory captured its first breathtaking images of the night sky, marking a significant step towards understanding our universe’s intricacies.
The LSST represents a monumental leap in astronomical research, blending wide-field and large-aperture telescope designs to investigate celestial objects that are typically faint and elusive. This integration of technology is designed to deliver unprecedented coverage of the sky, allowing researchers to observe everything from asteroid trajectories to the dynamics of our own Milky Way galaxy.
The Role of the LSST Camera in Astronomical Discoveries
The LSST camera, touted as the largest astronomical camera ever built, is central to the mission of probing the cosmos. With its capability to obtain images 21 times larger than its commissioning camera, the LSST camera is equipped for ‘cosmic cinematography.’ This term reflects its ability to create time-lapse images of the night sky every single night, capturing dynamic events and changes that occur in the universe. By transforming astronomical imaging into a cinematic exploration, the camera stands to revolutionize our understanding of cosmic phenomena.
The advanced technology behind the LSST camera allows for detailed investigations into various cosmological questions. From mapping the structure of the Milky Way to identifying potentially hazardous near-Earth objects, this camera significantly enhances the ability of astronomers to analyze vast swathes of data. The innovative combination of large light-gathering capabilities with expansive field views represents a new standard in astronomical observation.
Understanding Dark Matter through Advanced Imaging Techniques
Dark matter represents one of the greatest mysteries in astrophysics, constituting around 90% of the Milky Way’s mass while remaining undetectable by conventional means. The Rubin Observatory aims to tackle this enigma by utilizing the LSST camera’s precision imaging and data collection capabilities. This project could shed light on the gravitational effects of dark matter and provide key insights into its elusive nature.
By examining the interaction of light with cosmic structures, the observatory intends to pinpoint the locations and behaviors of dark matter across the universe. The unprecedented resolution offered by the LSST camera is expected to help scientists infer the presence and influence of this mysterious mass, leading to breakthroughs in our understanding of not just dark matter, but also the broader implications for cosmology and the universe’s expansion.
Mapping the Milky Way: A Ten-Year Journey
One of the primary goals of the Rubin Observatory is to produce a detailed map of the Milky Way galaxy over a ten-year period. This project will track the movement of stars, gas, and interstellar dust, providing a dynamic picture of our galactic home. The LSST camera’s high-resolution imaging is crucial for capturing the vast intricacies of the Milky Way, allowing astronomers to study its structure and evolution over time.
As the observatory continuously scans the sky, it will create a vast database of astronomical images that scientists can analyze for years to come. This long-term mapping initiative not only aims to enhance our understanding of our galaxy’s formation and behavior but also encourages collaborative research among scientists globally, fostering new discoveries and insights into the cosmos.
The Impact of Cosmic Cinematography on Astrophysics
Cosmic cinematography, a term coined to describe the LSST project’s approach to astronomical observation, opens new avenues for astrophysics. By capturing the night sky in time-lapse sequences, scientists will be able to scrutinize transient events such as supernova explosions and asteroid movements in ways never before possible. This technique will provide a more comprehensive understanding of cosmic events and their implications for our galaxy.
The practice of cosmic cinematography will not only transform how data is gathered but also how scientific narratives are constructed around cosmic phenomena. As researchers access a continuous stream of high-quality observational data, they will be equipped to build more detailed models of astrophysical processes, addressing fundamental questions related to the structure and dynamics of the universe.
Empowering Scientific Research with Open Data
A revolutionary aspect of the LSST project is its commitment to open data accessibility. Unlike traditional practices where data may be restricted to select researchers, the Rubin Observatory aims to make all collected astronomical images and data available to the global scientific community. This democratization of data is set to inspire innovation, allowing scientists from various disciplines to utilize the information for diverse research purposes, including understanding dark matter and cosmic structures.
This approach not only fosters collaboration among astronomers but also engages educational institutions, contributing to outreach efforts aimed at K-12 students. By implementing educational programs alongside data release, Rubin Observatory enriches public understanding of astronomy and inspires future generations of scientists, thereby ensuring that the 10-year mission has lasting impacts.
Preparing for the Main Camera Installation
As preparations for the main LSST camera’s installation progress, the team at the Rubin Observatory is enthusiastic about the capabilities it will bring. Expected to be operational by early 2025, this large camera will significantly enhance the telescope’s ability to collect data, ultimately pushing the boundaries of astronomical research. The anticipation surrounding the transition from the commissioning camera to the LSST camera marks a pivotal moment in the project’s timeline.
Once the main camera is integrated, the team will enter a commissioning period where they will fine-tune the instrument to ensure it meets the ambitious scientific goals set forth in the LSST project. This rigorous testing phase will be crucial to optimizing the camera’s performance, ensuring that it can accurately gather data over the ensuing years, ultimately enabling critical insights into dark matter and cosmic dynamics.
Challenges and Innovations in Astronomy
The LSST project does not come without its challenges, particularly given the sheer amount of data expected to be generated over its ten-year duration. The observatory must develop robust systems for data processing, storage, and dissemination to handle the influx of astronomical images and associated datasets. These challenges also present opportunities for innovation within the field of astronomy, particularly in the realm of data analytics and machine learning.
By addressing data management issues head-on, the Rubin Observatory is setting new standards for future projects. This commitment to overcoming obstacles with innovative solutions will not only benefit the LSST initiative but also serve as a model for upcoming astronomical endeavors, paving the way for an enhanced understanding of the universe and its fundamental mysteries.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Astronomical Research
As the Rubin Observatory embarks on its ambitious quest to map the universe, the implications of its research extend far beyond the immediate scientific community. The insights gained from the LSST project could have profound effects on our understanding of dark matter, the behavior of galaxies, and the fundamental laws governing our universe. With this in mind, the excitement surrounding the project continues to grow.
Looking ahead, the implications of the Rubin Observatory’s discoveries could lead to paradigm shifts in astrophysics. By unearthing the mysteries of dark matter and providing high-quality astronomical images for analysis, the LSST project promises to enhance our grasp of the cosmos while fostering a global spirit of collaboration and discovery among scientists dedicated to understanding the universe.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Rubin Observatory and its main purpose?
The Rubin Observatory, officially known as the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, is a groundbreaking facility dedicated to astronomy and astrophysics. Its main purpose is to conduct the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST), which aims to create a comprehensive map of the universe over a ten-year period, focusing on dark matter, dynamic celestial objects, and Milky Way mapping.
How does the LSST Camera at Rubin Observatory contribute to cosmic cinematography?
The LSST Camera at the Rubin Observatory is designed for ‘cosmic cinematography,’ allowing it to capture vast amounts of astronomical images simultaneously. Its high resolution and large aperture enable detailed observations of faint objects, significantly enhancing our ability to study the cosmos, including the mapping of the Milky Way and dark matter detection.
What are the significant milestones achieved by Rubin Observatory so far?
Rubin Observatory achieved a major milestone in October 2024 by capturing its first images of the night sky using the Commissioning Camera. The LSST Camera, the largest astronomical camera ever constructed, is being prepared for installation, with planned public releases of astronomical images expected in mid-2025.
How will Rubin Observatory help in understanding dark matter?
Rubin Observatory’s LSST will help understand dark matter by capturing detailed images of the universe. With its powerful imaging capabilities, it aims to reveal the gravitational effects of dark matter, which constitutes about 90% of the mass of the Milky Way, providing new insights into this elusive component of the universe.
What kind of data will Rubin Observatory provide to the scientific community?
Rubin Observatory will provide an extensive data set from its 10-year survey, making all astronomical images and findings immediately available to the scientific community. This open-access approach promotes collaborative research, encompassing various scientific interests from asteroid tracking to Milky Way structure mapping.
What is the significance of the Legacy Survey of Space and Time project?
The Legacy Survey of Space and Time project is significant because it combines wide-field observations with high-resolution imaging. This will allow astronomers to monitor the night sky for transient events, study dark energy, and gain a deeper understanding of the universe’s evolution over a decade, transforming how astronomical research is conducted.
When can we expect the first public release of astronomical images from the Rubin Observatory?
The first public release of astronomical images from the Rubin Observatory is anticipated in mid-2025. This will follow a six-month commissioning period for the LSST Camera, allowing scientists to start analyzing and utilizing the data gathered.
What educational outreach efforts are associated with the Rubin Observatory’s project?
The Rubin Observatory’s initiative includes educational outreach aimed at K-12 students and institutions across participating countries. The goal is to provide access to the observatory’s data, encouraging engagement and inspiration in astronomy and science among young learners.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Simonyi Survey Telescope | The telescope takes on-sky observations using a 144-megapixel test camera. |
| Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) | A 10-year project aiming to create a comprehensive map of the universe. |
| First Light Achievement | Captured its first images of the night sky in October 2024. |
| Data Accessibility | All data will be available to scientists and for educational outreach. |
| Dark Matter and Energy Research | Aims to investigate the nature of dark matter and dark energy. |
| First Public Release | Expected to occur in mid-2025 after a six-month commissioning period. |
Summary
The Rubin Observatory represents a groundbreaking leap in our understanding of the universe. By utilizing the powerful Simonyi Survey Telescope along with its advanced LSST camera, this observatory is set to revolutionize astronomical research over the next decade. The anticipated data will not only enhance our mapping of the Milky Way but also provide critical insights into dark matter and dark energy, crucial components in the cosmic puzzle. Emphasizing open data accessibility for the scientific community, the Rubin Observatory aims to foster collaboration and inquiry, paving the way for future discoveries that may reshape our understanding of the cosmos.